Petroleum Hydrocarbons Environmental contamination by petroleum hydrocarbons is the most common site contamination issue encountered by environmental professionals The nature of petroleum hydrocarbon contamination is highly variable Petroleum hydrocarbons themselves are diverse mixtures of chemical componentsHydrocarbons and petroleum are almost synonymous in environmental science Microbial production and consumption of hydrocarbons in the global ocean Nature Microbiology, 21;Many hydrocarbons occur in nature In addition to making up fossil fuels, they are present in trees and plants, as, for example, in the form of pigments called carotenes that occur in carrots and green leaves More than 98 percent of natural crude rubber is a hydrocarbon polymer, a chainlike molecule consisting

Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbon Wikipedia
Hydrocarbons in nature
Hydrocarbons in nature-Paraffin hydrocarbon, also called alkane, any of the saturated hydrocarbons having the general formula C n H 2n2, C being a carbon atom, H a hydrogen atom, and n an integer The paraffins are major constituents of natural gas and petroleumParaffins containing fewer than 5 carbon atoms per molecule are usually gaseous at room temperature, those having 5 to 15 carbon atoms areHydrocarbons are non polar by nature and will naturally repel polar water molecules This is where the hydrophobic effect got its name There are many types of hydrocarbons and they are classified into saturated hydrocarbons, unsaturated hydrocarbons, cycloalkanes and aromatic hydrocarbons



Hydrocarbon Creationwiki The Encyclopedia Of Creation Science
Dependency on hydrocarbons will therefore take a long time to change Shale gas has radically changed the picture on the natural gas side Demand and supply for hydrocarbons can be matched over time but the process will be bumpy, with oil prices in particular likely to remain volatile, within an overall upward trendOVERVIEW OF TOTAL PETROLEUM HYDROCARBONS This document presents information in a way that is more summary in nature than the usual comprehensive toxicological profile Total petroleum hydrocarbons (TPH) is such a broad family of compounds that it would be a large undertaking to present comprehensive environmental, chemical/physical, and healthThe order of substitution on aromatic compounds is governed by the nature of substituents present in the aromatic ring In electrophilic aromatic substitution reactions, a carbocation is generated while in nucleophilic aromatic substitutions, a carboanion is generated Hydrogenation reactions convert aromatic compounds into saturated compounds
Numerous petroleumgeochemical analyses of deeply buried, highrank, finegrained rocks from ultradeep wellbores by different investigators demonstrate that C 15 hydrocarbons (HCs) persist in moderate to high concentrations at vitrinite reflectance (R0) values of –50% and persist in measurable concentrations up to R0 = 70–80%, at which point theHydrocarbons are released into the ocean via natural oil seeps and industrial spills associated with extraction, transportation and consumption of oil, totalling ~13 Tg per year 1Methane (CH 4) is the main constituent of natural gas, while ethane (C 2 H 6) is used as a petrochemical feedstock Both of these hydrocarbons, and others
Total petroleum hydrocarbons (TPH) is a term used to describe a large family of several hundred chemical compounds that originally come from crude oil Crude oil is used to make petroleum products, which can contaminate the environment Because there are so many different chemicals in crude oil and in other petroleum products, it is notHydrocarbons are usually colourless, hydrophobic and have only weak odours We can find hydrocarbons in nature and besides fossil fuels, these are present in trees and plants For example, in carrots and green leaves, these are available in theHydrocarbons are naturallyoccurring compounds and form the basis of crude oil, natural gas, coal, and other important energy sources Hydrocarbons are highly combustible and produce carbon




Nature Chemistry A Bifunctional Catalyst Returns Co2 To The Gasoline Hydrocarbons From Whence It Came T Co Vvfjqfbtxk




The Dd Variations With Carbon Number Of Alkanes For Natural Gasses Download Scientific Diagram
Oeochlmica et Cogmochlmica Acta, 1972, Vol 36, pp 953 to 959 Pergamon Press Printed In Northern Ireland Ubiquity of hydrocarbons in nature Aliphatic hydrocarbons in weathered limestone D W NOONER, J OB6,* and J M GiBERTf Departments of Biophysical Sciences and Chemistry, and V L RAY and J E MANN Department of Biology, University ofR L McCarthy (unpublished) estimates that the integrated production of CCl 2 F 2 and of CCl 3 F, the two principal compounds of the class, was about one megaton of each in mid 1971;Aliphatic hydrocarbons ranging from C 13 to C 33 have been identified in dust Isoprenoids and other isomeric alkanes have also been detected in some of the dust samples The widespread occurrence of dust particles makes them a potential contaminant of extraterrestrial and geochemical specimens being analyzed for organic compounds <P />




Plot Of S 1 Versus Toc Wt Illustrating The Indigenous Nature Of Download Scientific Diagram
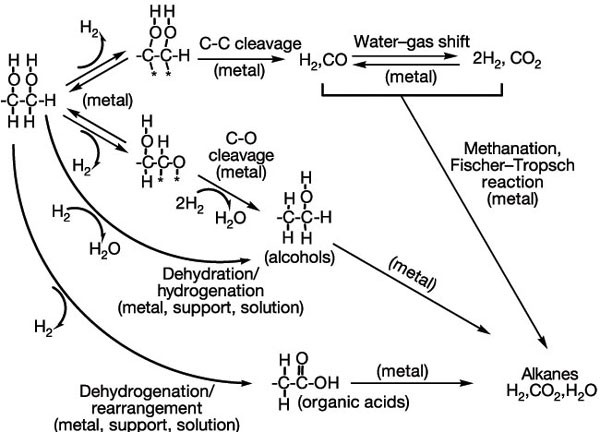



Hydrogen From Catalytic Reforming Of Biomass Derived Hydrocarbons In Liquid Water Nature
In organic chemistry, a hydrocarbon is an organic compound consisting entirely of hydrogen and carbon Hydrocarbons from which one hydrogen atom has been removed are functional groups, called hydrocarbyls Aromatic hydrocarbons (arenes), alkanes, alkenes, cycloalkanes and alkynebased compounds are different types of hydrocarbonsFormation of Hydrocarbons This section is a brief outline that primarily deals with the formation of the various hydrocarbons namely crude oil and natural gas in general The information is from Petroleum Geology for Geophysicists and Engineers by Richard SelleyPolycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons are primarily found in natural sources such as bitumen 26 27 PAHs can also be produced geologically when organic sediments are chemically transformed into fossil fuels such as oil and coal 28



1
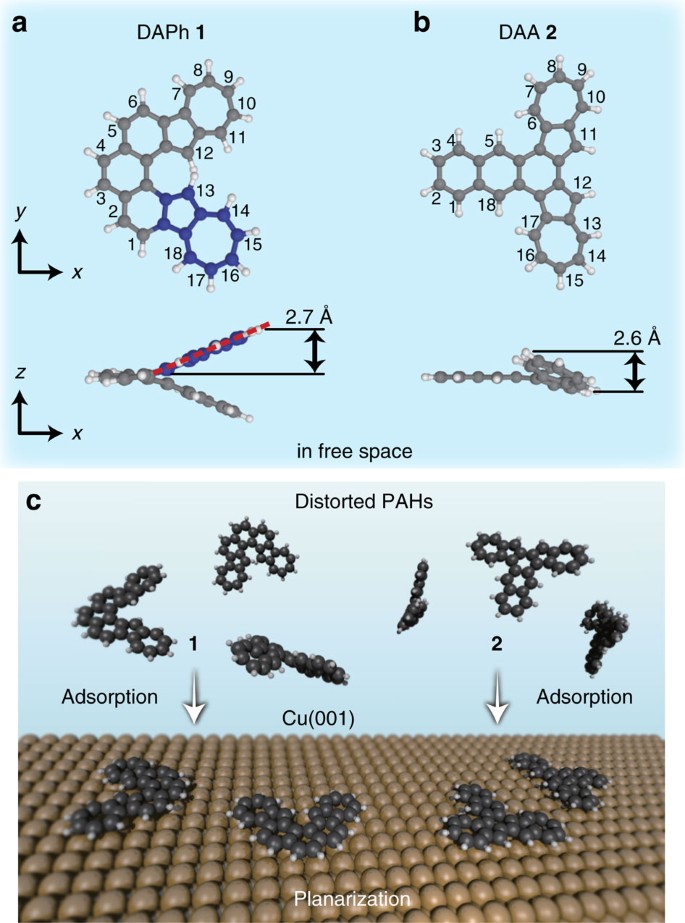



Strain Induced Skeletal Rearrangement Of A Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbon On A Copper Surface Nature Communications
Ubiquity of hydrocarbons in nature Aliphatic hydrocarbons in weathered limestone The aliphatic hydrocarbons in two specimens of limestone (one from Texas and the other from Italy) which were weathered in place as parts of building structures have been investigated using gas chromatography and gas chromatographymass spectrometryMore information Connor R Love et al Microbial production and consumption of hydrocarbons in the global ocean, Nature Microbiology (21) DOI /s Journal informationA hydrocarbon is a molecule whose structure includes only hydrogen and carbon atoms Interestingly, though, hydrocarbons (once combined) also form bonds with other atoms in order to create organic compounds
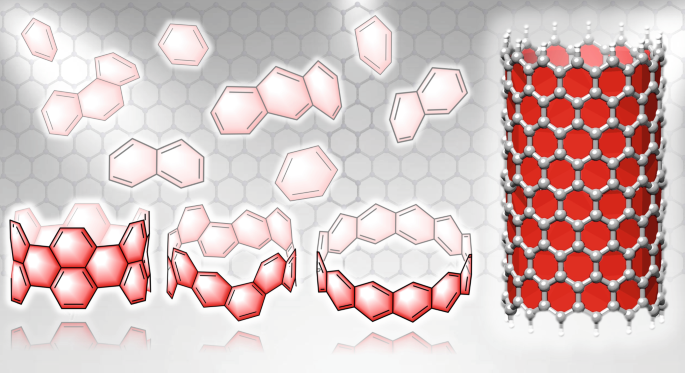



Aromatic Hydrocarbon Belts Nature Chemistry




Hydrocarbons And The Evolution Of Human Culture Nature
Hydrocarbon Hydrocarbons are compounds comprised exclusively of carbon and hydrogen and they are by far the dominant components of crude oil, processed petroleum hydrocarbons (gasoline, diesel, kerosene, fuel oil, and lubricating oil), coal tar, creosote, dyestuff, and pyrolysis waste products From Treatise on Geochemistry, 07Polynuclear aromatic hydrocarbons in Drinkingwater Background document for development of endorsed or recommended by the World Health Organization in preference to others of a similar nature that are not mentioned Errors and omissions excepted, theHydrocarbons like pyrene are organic compounds made up entirely of carbon and hydrogen Starting off from simple gases, Long Zhao/Ralf I Kaiser et al/Nature Astronomy
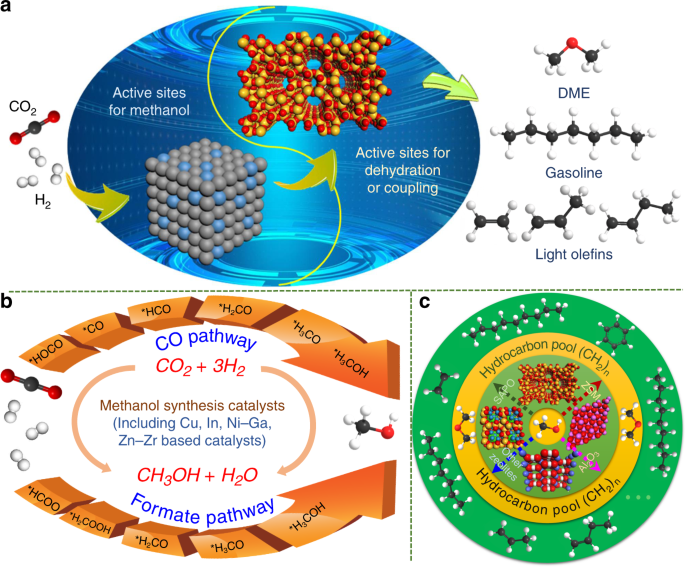



Co 2 Hydrogenation To High Value Products Via Heterogeneous Catalysis Nature Communications



2
The hydrocarbons extracted from 057 g of this sample range from C^, to 034 and show a maximum at 037, with a clear pre dominance of odd over even alkanes above n023 A similar range of hydrocarbons was obtained from an extract of 02 g of dust collected in the laboratory in January, 1965 (Fig 1B;The simplest Hydrocarbon is methane, CH 4 This is the simplest member of a series of hydrocarbons regardless of its nature 6 Because the triple bond is linear, it can only be accommodated in rings larger than ten carbons In simple cycloalkynes the triple bond carbons are assigned ring locations #1 and #2 Which of the two is #1 may beNaturalgas processing is a range of industrial processes designed to purify raw natural gas by removing impurities, contaminants and higher molecular mass hydrocarbons to produce what is known as pipeline quality dry natural gas Naturalgas processing begins at the well head The composition of the raw natural gas extracted from producing wells depends on the type, depth,



1
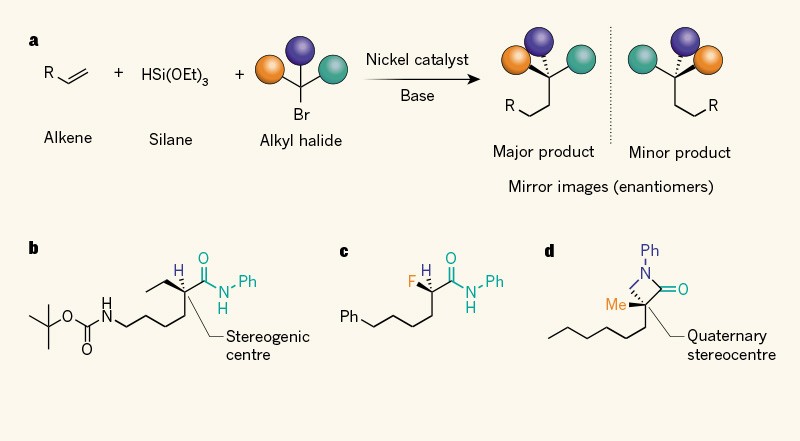



Practically Simple Reactions Convert Hydrocarbons To Precious Chemicals
Benzene was once a common additive in gasoline, but due to the discovery of its carcinogenic nature in humans, it's use has been reduced to mainly high octane fuels Aromatic hydrocarbons arePetroleum Petroleum Origin of hydrocarbons Although it is recognized that the original source of carbon and hydrogen was in the materials that made up primordial Earth, it is generally accepted that these two elements had to pass through an organic phase to be combined into the varied complex molecules recognized as hydrocarbons The organic material that is the source of mostMeasurement methods vary between countries, between provinces and states within a country, and even tailored for a specific location, depending on the nature of the PHCs The simplest method is called total petroleum hydrocarbons (TPH), which is an estimated value for the total of PHCs




Oil And Gas Industry Overview
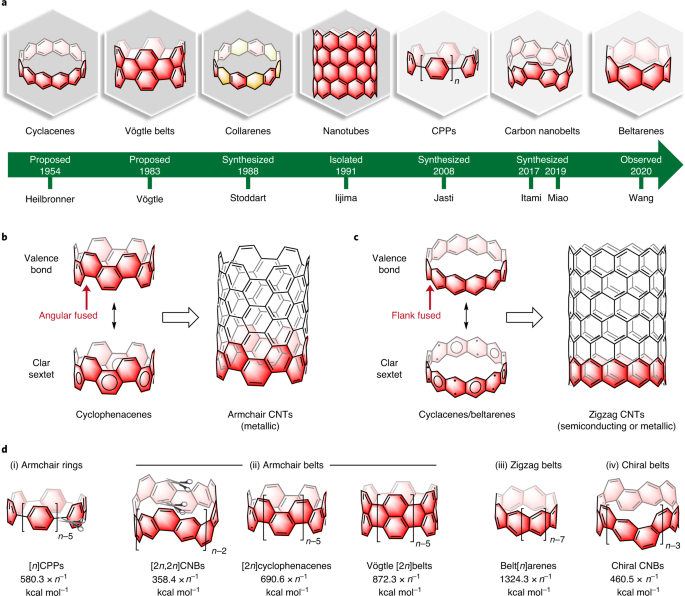



Aromatic Hydrocarbon Belts Nature Chemistry
Petroleum (/ p ə ˈ t r oʊ l i ə m /), also known as crude oil and oil, is a naturally occurring, yellowishblack liquid found in geological formations beneath the Earth's surface It is commonly refined into various types of fuelsComponents of petroleum are separated using a technique called fractional distillation, ie separation of a liquid mixture into fractions differing in boilingChlorinated hydrocarbons are organic molecules characterized by the presence of at least one chlorine atom bonded to a carbon atom In some cases, chlorinated hydrocarbons are made in nature They are naturally present in a number of animals, and sometimes appear as byproducts of events like firesComplex hydrocarbons and their derivatives are found throughout nature for example, is a hydrocarbon that contains long chains of alternating C=C double bonds and CC single bonds Writing the structure of complex hydrocarbons can be simplified by using a line
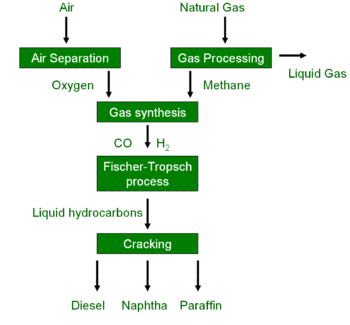



Gas To Liquids Wikipedia




Hydrocarbon Wikipedia
Polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs) are considered the most toxic component of oil yet baseline data measuring oil exposures andNatural sources of hydrocarbons Oil spills are always thought of as affecting an otherwise hydrocarbonfree marine environment so the percentage of discharge from "natural sources" may come as a surprise to some readers Various coastal areas located around eroded sedimentary basins or faults between plates of the Earth's crust harbour natural seepage of fossil fuelsMost petroleum arises from the thermal alteration of organic matter in finegrained sedimentary rocks The time–temperature conditions of petroleum



Pinkmonkey Com Chemistry Study Guide 13 5 Hydro Carbons




Nature Insight Hydrocarbon Reservoirs
Concerns about the depletion of fossil fuel reserves and the pollution caused by continuously increasing energy demands make hydrogen an attractive alternative energy source Hydrogen is currentlyThe most common kind of hydrocarbon ring present in nature is aromatic hydrocarbon ringThis aromatic hydrocarbon ring has a very wide range of applications Some of these are given belowIt has been shown that a large body of evidence on the sources, transformation, and migration of hydrocarbons in soils has been acquired by different researchers Available data about the origin and behavior of hydrocarbon gases, total petroleum hydrocarbons, polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons, alkanes, and other compounds have been



2




Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbon Wikipedia



1 Carbon Cycle Oxidation Of Hydrocarbons To More Stable Compounds Download Scientific Diagram




Diamondoid Hydrocarbons Delving Into Nature S Bounty Science



1




On The Nature Of Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbons Associated With Sporting Walkways Dust Concentrations Sources And Relative Health Risk Sciencedirect
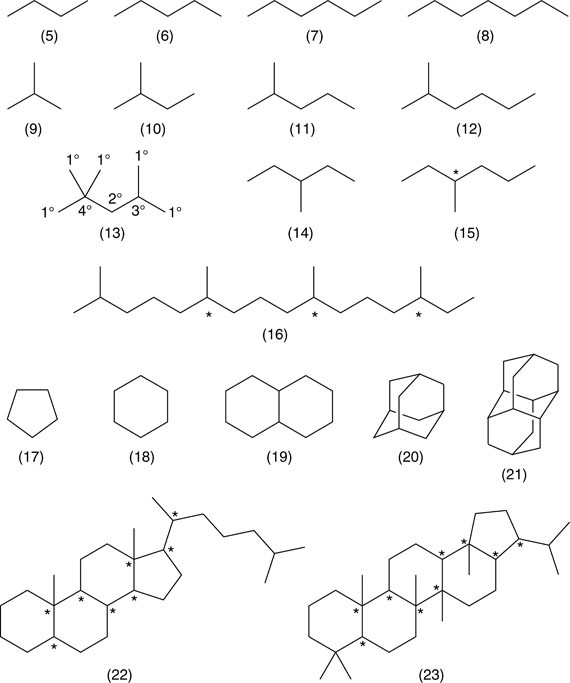



Hydrocarbons An Introduction To Structure Physico Chemical Properties And Natural Occurrence Springerlink




Hydrocarbon Definition Types Facts Britannica




Pdf The Binding Nature Of Light Hydrocarbons On Fe Mof 74 For Gas Separation Semantic Scholar




Formation Of Diamonds In Laser Compressed Hydrocarbons At Planetary I
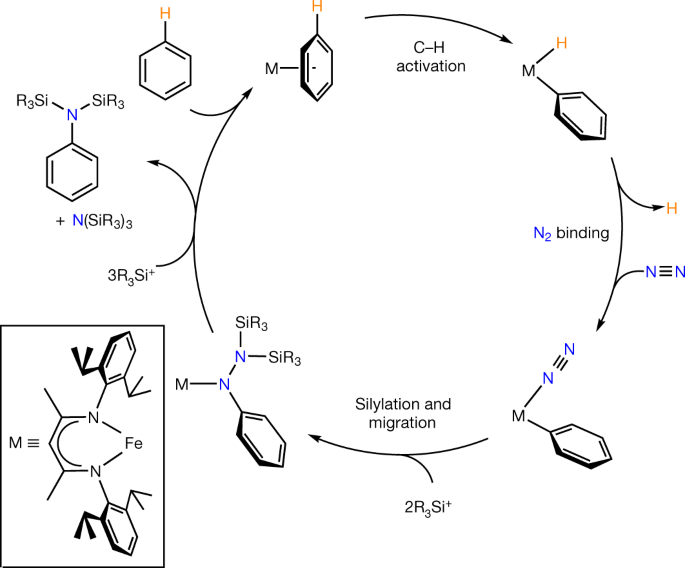



Coupling Dinitrogen And Hydrocarbons Through Aryl Migration Nature




A Metal Free Electrocatalyst For Carbon Dioxide Reduction To Multi Carbon Hydrocarbons And Oxygenates Topic Of Research Paper In Nano Technology Download Scholarly Article Pdf And Read For Free On Cyberleninka Open Science Hub




Wave Nature Of Delocalized Electrons In Defective Hydrocarbons At The Origin Of Cosmic Infrared Emission




Pdf The Oxidation Of Hydrocarbons By Diverse Heterotrophic And Mixotrophic Bacteria That Inhabit Deep Sea Hydrothermal Ecosystems
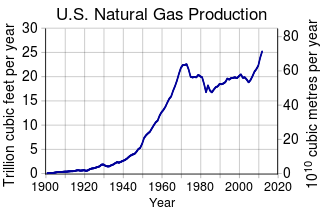



Natural Gas Wikipedia




Hydrocarbon Gases An Overview Sciencedirect Topics




Transformations Of Petroleum Hydrocarbons In Nature Chemical And Biochemical Alteration Of Crude Oils Springerlink




A Squalene Synthase Like Enzyme Initiates Production Of Tetraterpenoid Hydrocarbons In Botryococcus Braunii Race L Nature Communications X Mol



Coupling Dinitrogen And Hydrocarbons Through Aryl Migration Nature Index




Nature Chemistry Odd Even Alternations In Helical Propensity Of A Homologous Series Of Hydrocarbons T Co Lcrrkpmsor




Hydrocarbon Definition Types Facts Britannica




Figure 4 From Microbial Metabolism Of Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbons Pahs A Review Semantic Scholar




Hydrocarbon Rings Hydrocarbons From Earth S Crust Ppt Video Online Download



Hydrocarbon Creationwiki The Encyclopedia Of Creation Science




11 Chemistry Notes Ch13 Hydrocarbons
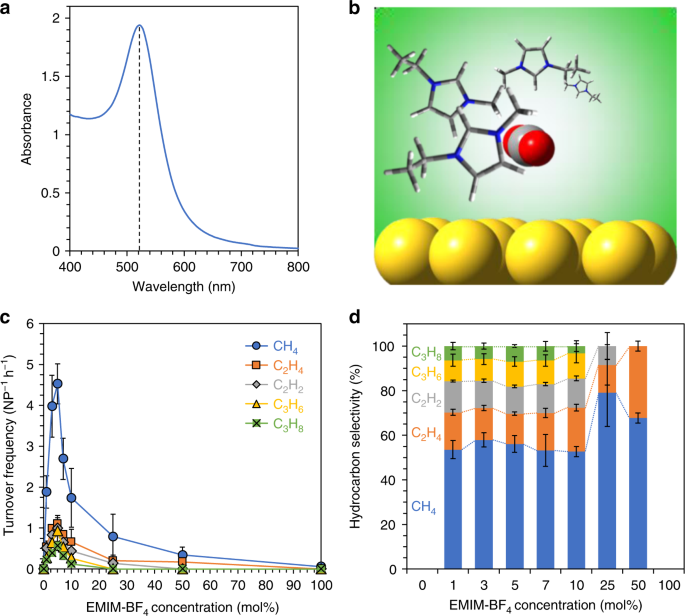



Plasmonic Photosynthesis Of C 1 C 3 Hydrocarbons From Carbon Dioxide Assisted By An Ionic Liquid Nature Communications



2




Abiogenic Deep Origin Of Hydrocarbons And Oil And Gas Deposits Formation Intechopen




Cyclic Hydrocarbons




Red Basil Herbs Spice Plant The Smell Of Aromatic Hydrocarbons Kitchen Nature Pikist




Nature Geoscience Ngeo Degradation By Microorganisms Can Remove Aromatic Hydrocarbons From The Oceans T Co Xcriqc4hs1



Turning On Hydrocarbons Nature Chemistry




Hydrocarbons Anjung Sains Makmal 3
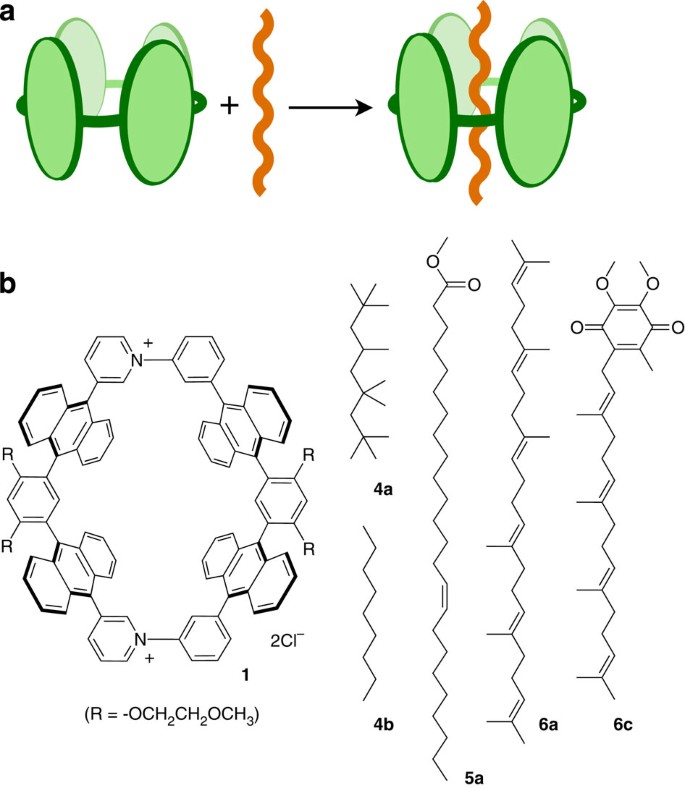



A Polyaromatic Molecular Tube That Binds Long Hydrocarbons With High Selectivity Nature Communications




Natural And Waste Hydrocarbon Precursors For The Synthesis Of Carbon Based Nanomaterials Graphene And Cnts Sciencedirect
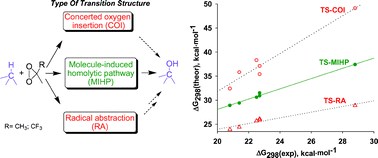



Oxidation Of Some Cage Hydrocarbons By Dioxiranes Nature Of The Transition Structure For The Reaction Of C H Bonds With Dimethyldioxirane A Comparison Of pw91 Density Functional Theory With Experiment Organic




Stratigraphy And Hydrocarbons Erth 1010 1100 Deposition This




Natural Gas Wikipedia
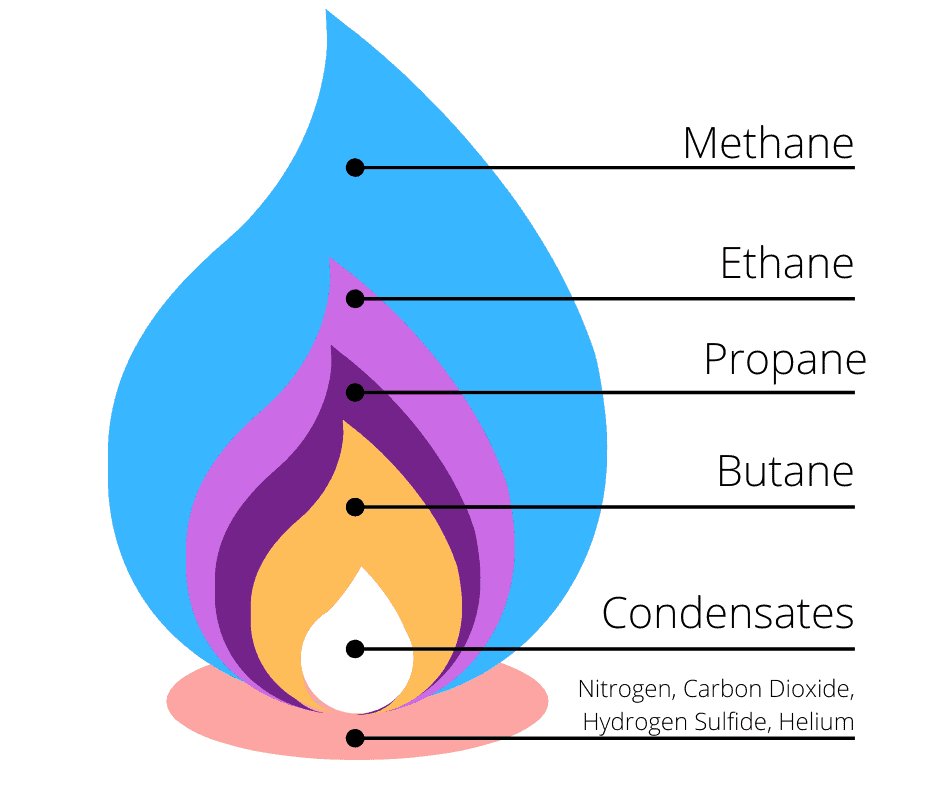



Natural Gas Composition
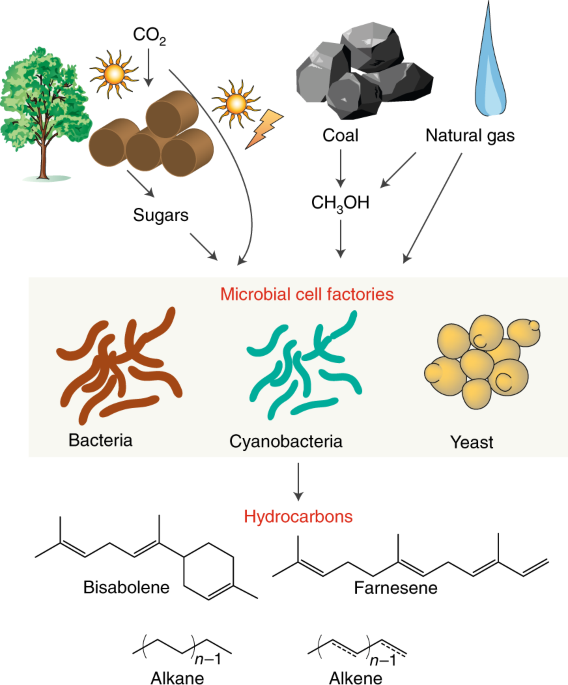



Barriers And Opportunities In Bio Based Production Of Hydrocarbons Nature Energy




Hydrocarbon Wikipedia




Hydrocarbons Benefits Risks Posts Facebook




Nature Catalysis June Issue Out Now Fe S Clusters To Reduce Co2 To Hydrocarbons See Cover Also Inside Iron Catalysed Suzuki Couplings Photocathode Design For Inexpensive Water Splitting Reviews On Methanol To Hydrocarbons And




What Are Natural Gas Liquids And How Are They Used Today In Energy U S Energy Information Administration Eia



1




Isotopic Evidence For Quasi Equilibrium Chemistry In Thermally Mature Natural Gases Pnas




What Are Hydrocarbons Discuss Their Classification From Chemistry Organic Chemistry Some Basic Principles And Techniques Class 11 Rajasthan Board English Medium




Do Not Explore Or Exploit Hydrocarbons In The Tariquia Nature Reserve In Tarija
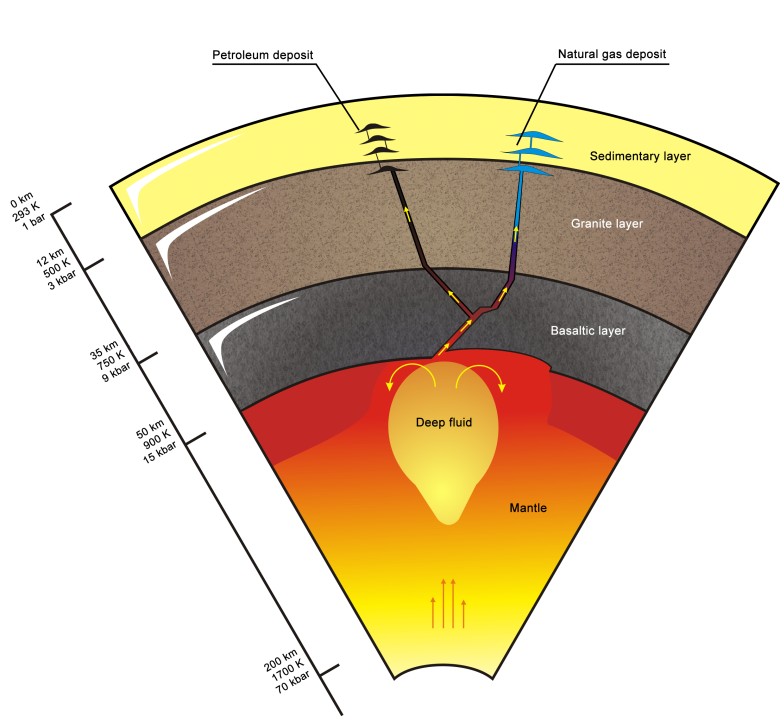



Abiogenic Deep Origin Of Hydrocarbons And Oil And Gas Deposits Formation Intechopen




Remote Carboxylation Of Halogenated Aliphatic Hydrocarbons With Carbon Dioxide Nature Nature Research Chemistry
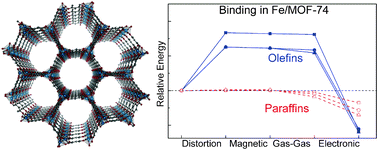



The Binding Nature Of Light Hydrocarbons On Fe Mof 74 For Gas Separation Physical Chemistry Chemical Physics Rsc Publishing
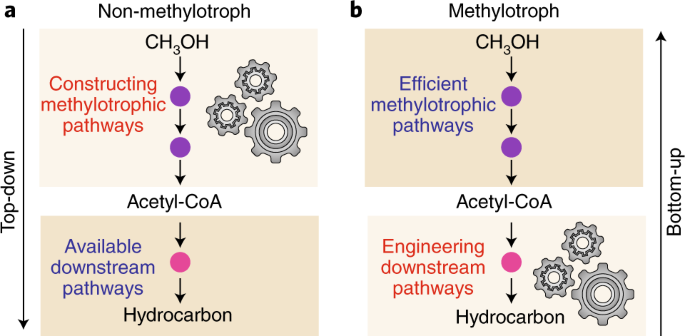



Barriers And Opportunities In Bio Based Production Of Hydrocarbons Nature Energy
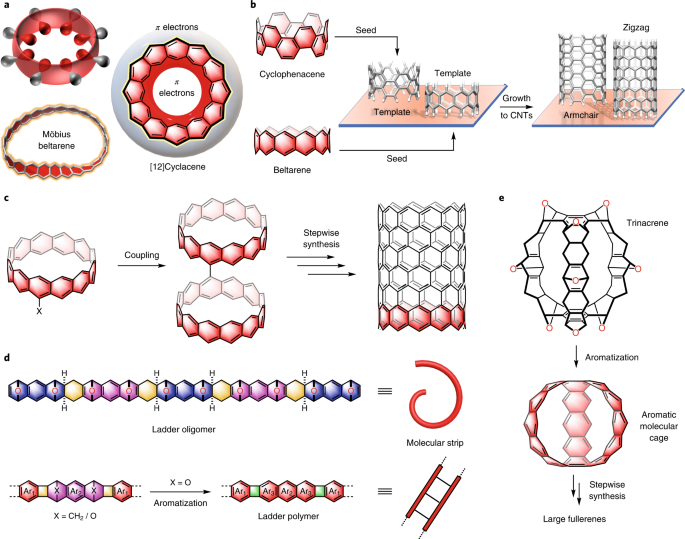



Aromatic Hydrocarbon Belts Nature Chemistry




The Future Of Natural Gas Pricing Farewell To Groningen Energy Europe




Plot Of S1 Versus Toc Illustrating The Indigenous Nature Of Download Scientific Diagram




A Methadone Plan For The World S Hydrocarbon Addiction




The Green Origin Of Hydrocarbons




Nature Catalysis June Issue Out Now Fe S Clusters To Reduce Co2 To Hydrocarbons See Cover Also Inside Iron Catalysed Suzuki Couplings Photocathode Design For Inexpensive Water Splitting Reviews On Methanol To Hydrocarbons And
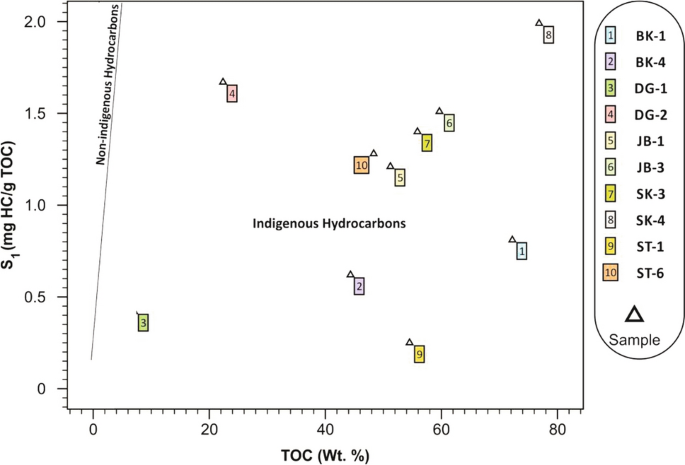



Source Rock Potential Assessment Of The Paleocene Coal And Coaly Shale In The Attock Cherat Range Of Pakistan Springerlink




What Is Hydrocarbon



Terry Mcgenity Cyanobacteria Release 100 Times More Hydrocarbons Into The Ocean Than All Petroleum Sources A Cryptic Microbial Cycle Stops These Hydrocarbons Accumulating In The Sea A Brief Commentary T Co Ltjyttq3qy




Dill Garden Spice Kitchen Green Eating Aromatic Hydrocarbons Plants Koper The Smell Of Nature Pikist



Natural Sources Of Hydrocarbons Pollution Black Tides




Plot Of S 1 Versus Toc Wt Illustrating The Indigenous Nature Of Download Scientific Diagram




Chapter 25 Hydrocarbon Compounds Ppt Download




Hydrocarbon Gas Liquids Explained U S Energy Information Administration Eia




Biodegradation Hydrocarbons Enviro Wiki
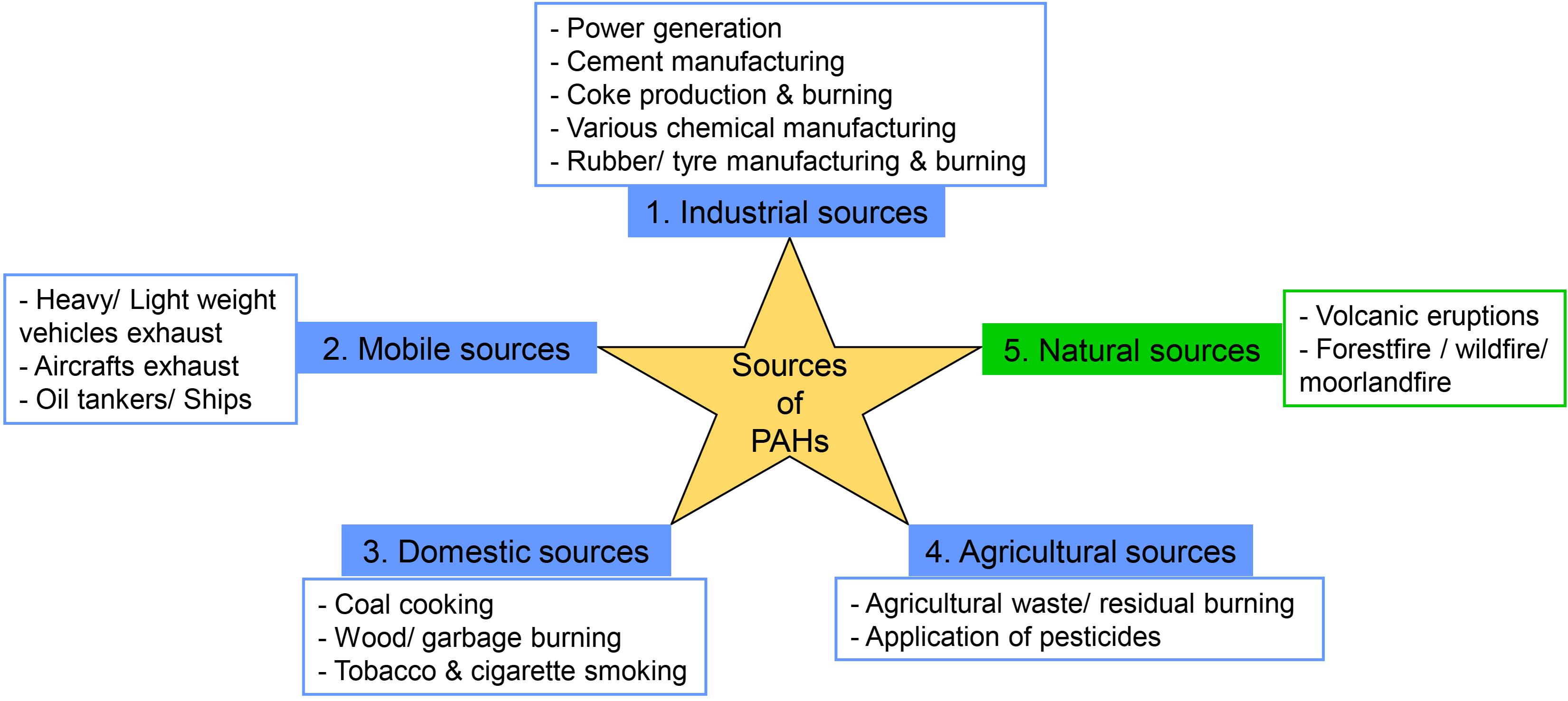



Frontiers Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbons Sources Toxicity And Remediation Approaches Microbiology




The Mechanisms Of Asphaltene Precipitation Concerning The Nature In Download Scientific Diagram



Link Springer Com Content Pdf 10 1007 978 3 319 2 4 Pdf



What Are Hydrocarbons Gulf Coast Environmental Systems




Chapter Organic Chemistry Alkanes And Aromatic Hydrocarbons Cycloalkanes




Hydrocarbon Definition Types Facts Britannica




How We Obtained The Abnormal Nir Absorbing Hydrocarbon Nature Portfolio Chemistry Community




Hydrocarbon Definition And Examples Market Business News




Electronic Processes In Paraffinic Hydrocarbons Part 1 On The Nature Of Carrier Traps Transactions Of The Faraday Society Rsc Publishing




Pdf Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbons Bioaccumulation In Dragonfly Nymphs Anisoptera And Determination Of Alkylated Forms In Sediment For An Improved Environmental Assessment




Oil And Gas Industry Overview




Energy Hydrocarbons
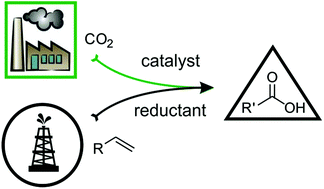



Carboxylic Acid Derivatives Via Catalytic Carboxylation Of Unsaturated Hydrocarbons Whether The Nature Of A Reductant May Determine The Mechanism Of Co2 Incorporation Dalton Transactions Rsc Publishing
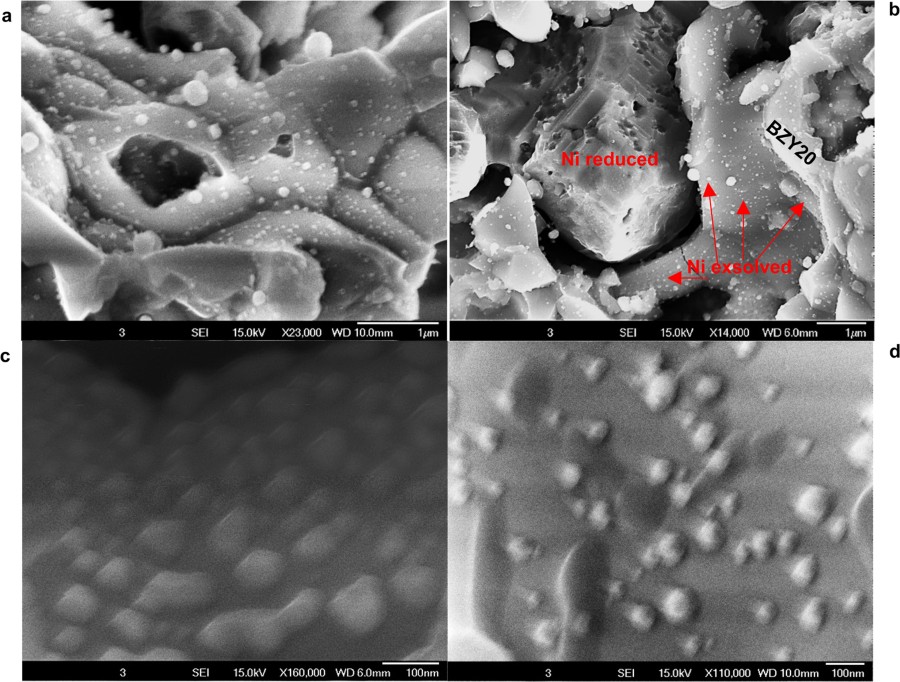



Extended Data Fig 6 Sem Image Of The Anode Of A Pcfc After Running For 1 400 And 6 000 H On Hydrocarbons At 500 C Nature




Odd Even Alternations In Helical Propensity Of A Homologous Series Of Hydrocarbons Request Pdf




Source Apportionment Of Sedimentary Hydrocarbons In The Segara Anakan Nature Reserve Indonesia Sciencedirect




Percentage And Nature Of Hydrocarbons With Zsm 5 And Cta Pom Download Table




Doc Aliphatic Hydrocarbons Saheed Abdulazeez Academia Edu




Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbon Formation Chemistry In A Plasma Jet Revealed By Ir Uv Action Spectroscopy Nature Communications X Mol


